

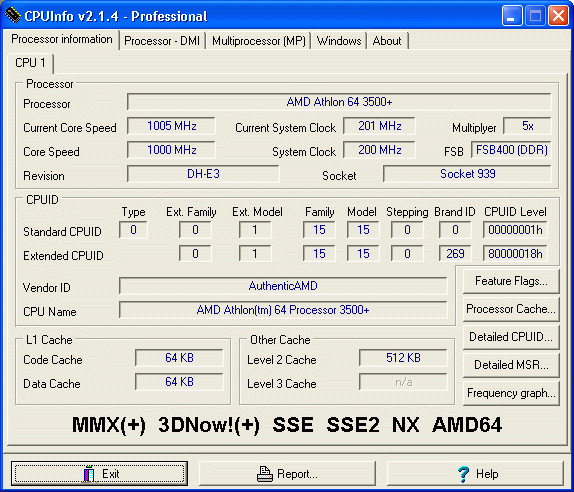
Other commands to check CPU information in Linux In my opinion, lscpu command is more than enough to give you all the information you need. This picture summarizes the most important processor information you get from the lscpu command. The last line is the list of feature flags that are manufacturer specific. Next is NUMA node for each CPU (both logical and physical CPUs). Read this wiki page to get quick info on CPU caches. It has L1D (data cache) of 32K, L1I (instruction cache) of 32K, L2 cache of 256K and 元 cache of 3072K. Virtualization is VT-x and is used to “help accelerate virtual machines created in VirtualBox, VMware, Hyper-V, and other apps”. The current clock speed of my CPU is 900.054 MHz whereas its maximum capacity is 3100 MHz and 400 MHz.īogoMIPS is “the number of million times per second a processor can do absolutely nothing”. Stepping is a number used by Intel to identify what level of design change a microprocessor was built to. The CPU model number is 142 (not relevant in my opinion) and the model name is Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-7200U CPU 2.50GHz (most important info). There is one NUMA node, the vendor is Intel and the CPU family is 6. And thus my dual core system is seen as having 4 CPUs by the operating system. In short, my system has one chip that contains two physical CPUs and each CPU is divided into two logical CPUs. The threads share physical execution resources of the physical core but the operating system sees them as separate cores. the actual physical CPUs.Īnd as you can see, each core has two threads. This tells you the number of real cores i.e. It means that the single chip has two physical CPUs on it. My system has 1 socket here which means it has one single chip for the CPUs. This picture from Intel also helps in visualizing what socket, CPU, core, threads mean. I would suggest reading this article to understand a bit about processors. The next 4 lines tells you about the number of processors, CPUs/cores and threads.
Which means that bytes are arranged as per Little Endian order.

#Cpuinfo aes instructions install
In other words, you can install both 32-bit and 64-bit operating systems on it.īyte order is Little Endian.
#Cpuinfo aes instructions 64 Bit
The CPU op-mods are 32 bit and 64 bit meaning that it can operate both as a 32-bit and 64-bit processor. The architecture for my system is 64-bit. The information is too technical so you should have some basic understanding of the terms here. I can go and search on the web for this model number to get more information.īut what does other fields in the output mean? What information do you really have about the processor here? Let me explain it to you. Well… that’s the processor information for my system and it should look somewhat similar for your Linux system as well.Īs you can see, the most important information is that my system has Intel i5-7200U processor. Model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-7200U CPU 2.50GHzįlags: fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush dts acpi mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht tm pbe syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc art arch_perfmon pebs bts rep_good nopl xtopology nonstop_tsc cpuid aperfmperf tsc_known_freq pni pclmulqdq dtes64 monitor ds_cpl vmx est tm2 ssse3 sdbg fma cx16 xtpr pdcm pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand lahf_lm abm 3dnowprefetch cpuid_fault epb invpcid_single pti ssbd ibrs ibpb stibp tpr_shadow vnmi flexpriority ept vpid fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 avx2 smep bmi2 erms invpcid mpx rdseed adx smap clflushopt intel_pt xsaveopt xsavec xgetbv1 xsaves dtherm ida arat pln pts hwp hwp_notify hwp_act_window hwp_epp flush_l1d It’s easier to remember as well because it is similar to the ls command. You can see the architecture of your system, number of processors, vendor information, cache information, processor speed etc. This is the simplest command that shows the CPU information in a simple and concise output. I’ll show you my favorite tool for this task along with a few additional ways to check CPUs in Linux. There are a number of ways you can get information about the processor on your Linux system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
